Falls in Elderly from Balance Disorder – Global Concern
To better understand what and how Balance Disorder affects elderly people, first let us understand what a fall is.
The World Health Organization defines falls as a sudden, uncontrolled descent of a person to the ground or floor or other lower level.
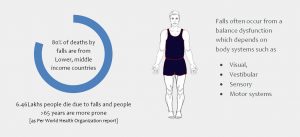
Falls are the second leading cause of accidental or unintentional injury-related deaths worldwide. Falls are also more common in low- and middle-income countries.
Adults greater than 65 years of age are at increased risk of falling. Falls in older adults often result in severe injuries, higher morbidity, and even death.
World health organization reports an estimated 6,46,000 individuals die from falls globally of which over 80% are in low- and middle-income countries.
Balance problems in older adults lead to falls. Balance is multifaceted. Several body systems (Visual, Vestibular, Sensory and Motor systems) work together to maintain a person steady.
Visual System- Precautions to avoid falls:
As older adult ages, visual acuity decreases from cataracts, glaucoma or macular degeneration. Frequent eye checkups to address the visual problem and making home modifications are essential for preventing falls.
A few common home modifications would be
- Color the edge of stairs with contrasting colors to overcome the loss of depth perception
- Remove cords, floor rugs
- Keep home free of clutter.
Medical Management Includes:
- Schedule regular eye check-ups.
- Have cataracts surgically corrected by the eye doctor.
Personal/ Lifestyle Modification:
- Be mindful of the loss of peripheral visual field deficit.
- Avoid driving at night
Vestibular System- Precautions to avoid falls
There are two balance organs called vestibular organs one in each ear.
As we walk and move, we look at several things in the environment. Our vestibular system and brain work together to help our eyes opposite to the head movement. This helps us to see our environment clearly.
In older adults, the vestibular system also functions lower than expected. The impulses traveling between the eyes and head(brain) are slower and the environment appears blurry or hazy. Patients often report this as feeling cloudy or hazy.
BPPV( Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) is another condition of the vestibular system where the crystals in the inner ear move out of place. A person experiences vertigo or room spinning in activities that require turning the head like rolling in bed or bending and lifting. Such patients are at a very high risk of falls.
Recommendations:
- Physical therapy treatment with re-positioning of the crystals can immensely help such patients.
Sensory System- Recommendations to avoid falls:
The incidence of Type 2 Diabetes increases with age, and many older adults have a co-existing diabetic neuropathy as a complication of diabetes.
The feet, toes feel numb and tingling and lose protective sensation of deep pressure. As a result, a person experiences difficulty feeling the ground. Patients with sensory loss also demonstrate a delay in recovering balance in the event of a misstep.
Some patients may also lose sensation to differentiate hot from cold adding to skin breakdown and wounds from the loss of protective sensation.
Recommendations:
- Stretch calf muscles and strengthen foot and toe muscles.
- Ensure proper foot care by wearing protective shoes,
- Treat callus regularly.
Motor System- Recommendations to avoid falls:
An optimal muscle strength is required for an individual to carry on his daily tasks of household and community mobility. As an adult age, he or she loses muscle strength. Research states that a decline in muscle strength starts at a rate of 12-15% per decade from 50 years and plateaus at 80 years of age. If the loss of muscle strength is beyond a certain threshold an individual has trouble standing, walking, climbing stairs, sit to stand from a chair, etc., The loss of muscle strength can be reversible with strengthening exercises carefully monitored by a physical therapist or strength conditioning specialist.
Recommendations:
- Including strengthening exercises of both proximal and distal muscles such as calf and toe muscles in addition to hip and core muscles helps improve the ability to stand on one leg and maintain balance during functional mobility tasks.
- Regular stretching exercises to overcome muscle shortening is crucial to generate good muscle contraction.
Summary:
Further, an individual is more likely to experience a recurrent fall if he has fallen once in the past 6 months. Fear of falling can be further disabling and can lead to a sedentary life when not addressed. A comprehensive evaluation of the multifaceted areas of balance is key in establishing an effective treatment plan.
If you or your loved one is experiencing any problems in the above areas, and you are seeing a gradual decline in their balance and If you feel that they are at risk of falls, please do seek the expertise of a physical therapist specialized in treating balance disorder.
Author:

Asha Gummadi Founder of TherexPortal
Asha J Gummadi, PT, MS, NCS, CKTP.
Asha is the founder of an award-winning website called TherexPortal, which helps rehabilitation clinicians such as physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and speech-language pathologists treat patients in rural India by issuing exercises in local languages. She has won the prestigious National Geographic Chasing Genius Challenge for her idea to bridge the rehabilitation shortage using technology. In her 15 years of clinical practice, Asha has gained most experience in the field of neuro-rehabilitation. In addition to being a board-certified Neurological Clinical Specialist, Asha also holds several advanced certifications to treat patients with neurological injuries. Her clinical areas of interest include Stroke, Parkinson’s Disease, Vestibular rehabilitation, Gait, and Balance Dysfunction. Asha is passionate about sharing knowledge and mentoring/teaching students and fellow clinicians Internationally through Sarojini E-learning, LLC and enjoys spending time with her family.
